- Blog
- 5 Challenges Address Validators Solve for P2P Marketplaces
5 Challenges Address Validators Solve for P2P Marketplaces
When it comes to reducing fraud and improving customer confidence, address validators are an essential piece of the puzzle. Here are five use cases for using them in your P2P marketplace.
Subscribe to the Incognia Newsletter
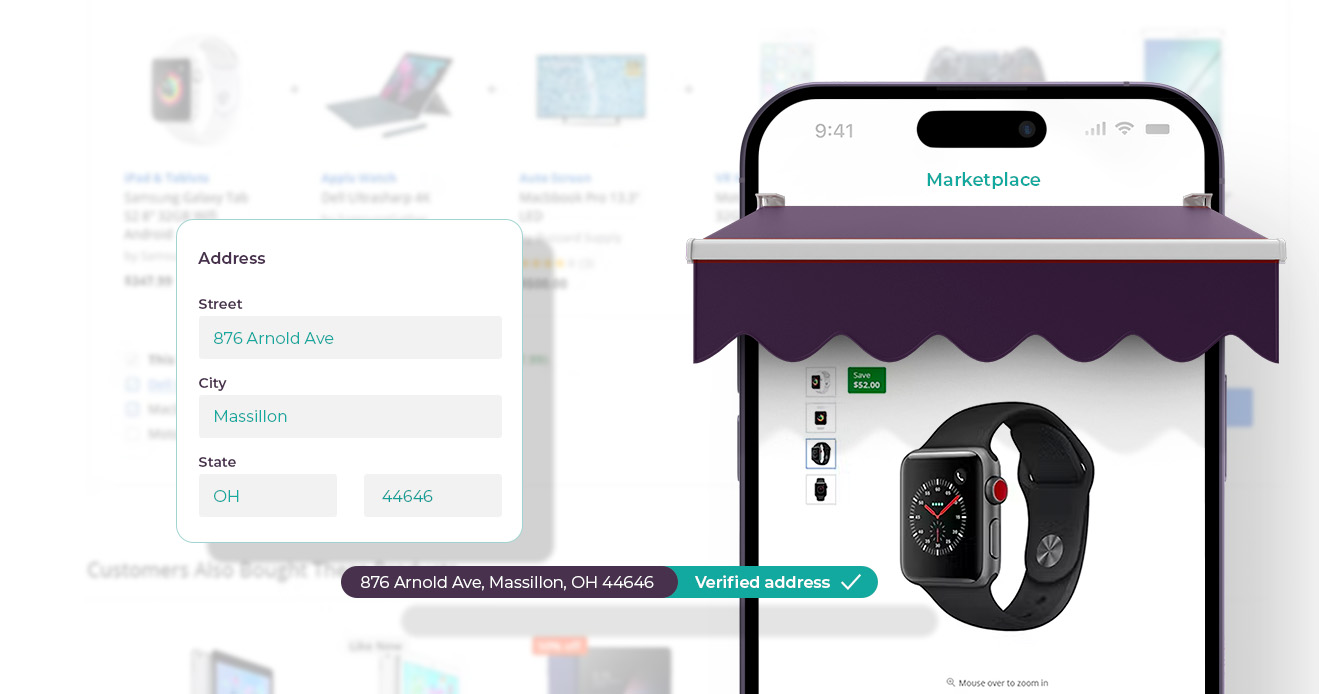
Address validation software is a mailing and shipping solution that uses centralized databases to validate addresses, confirming they’re both real and deliverable. These address validators are typically one component of extensive user and listing verification workflows used by P2P marketplaces to maintain trust on the platform and prevent scams.
A related process, known as address verification, takes addresses that have been validated and compares them to an authoritative database to verify the identity of the new buyer or seller. Address validation and verification can help P2P marketplaces meet the challenges of increasing scams and policy abuse without compromising the app experience for legitimate users.
Address validation for increased trust
P2P marketplaces design new user verification flows to increase trust and safety without causing further user frustration. Measures like address validation, email verification, and any additional identity verification are meant to culminate in a badge of trust for other platform users: in many cases, a literal, digital badge on a user’s profile. Seeing a visual indication of verified identity like this boosts trust and helps the marketplace community feel more confident buying and selling.
Validating addresses is a straightforward way that P2P marketplaces can determine the trustworthiness of a new user. Scammers will try to hide their true identity wherever possible, so determining whether the address they provide is an actual mailing address is a useful and frictionless first step towards verifying a new user.
More robust address verification measures can be the next step in the verification flow if the address validation shows inconsistencies. This way, address validators can reduce resources spent on document and selfie reviews.
In a high-friction example of an address verification flow, the platform could ask users to submit a photo of their driver’s license or passport to be cross-referenced against a national address database or a recent selfie. While address validation is less resource-intensive, it’s still possible to move on to address verification without adding user friction.
For example, real-time address verification allows platforms to check a user’s location in real-time at onboarding passively. That collected location information is then compared to the address the user provided.
Most people initiate sensitive processes like account creation and money transfers from “trusted locations,” like their homes. That means the passive location data gathered at onboarding will likely match the provided home address. If it does, address verification is complete without requiring additional user input.
Listing verification with validated addresses reduces marketplace scams
Some P2P marketplaces are based on proximity, meaning users transact with other users within a relatively small radius. Spoofing location to target regions of the marketplace far from their true location is a popular scammer tactic. Still, address validation helps put a stop to it by requiring an actual address.
For example, with address validation in place, a person living in Kansas couldn’t make up a random address in New York City and create fraudulent listings. When fraudsters can’t safely fake their location, their ability to scam other users, and the marketplace, plunges. Address verification can produce even more trustworthy user listings by proving that not only is the address real, but the user who claims to live there truly does.
Validating addresses means better shipping
Validating an address means verifying that it’s a real, deliverable address, but it can also help verify that an address is correct before shipping. By standardizing address information and prompting customers to enter corrections where relevant, P2P marketplaces can avoid misdeliveries that are inconvenient for sellers and buyers alike.
When a buyer accidentally puts in the wrong address and the seller ships to it, the buyer misses out on their package, and the seller might be asked to send a refund or a replacement, eating into their profit margin. If the package is returned to the sender, the buyer has to pay shipping fees again and deal with a long turnaround time, dampening the user experience.
Address validation helps catch these mistakes before shipping, meaning a cheaper, better user experience for everyone involved.
Users can trust reviews from validated addresses
When there’s no ID verification at onboarding, bad actors can create dozens of fake accounts and target other users by leaving phony one-star reviews. This attack, known as review sabotage, negatively impacts the user’s ability to sell or even buy on the platform, despite no wrongdoing on their part.
If in place, address validation and verification not only stop bad actors from using the same fake accounts to leave bad reviews but also from inflating seller ratings by posting false positive reviews. When bad actors have to validate addresses at onboarding, making fake accounts is more complicated. The fraudster is forced to choose between assigning all accounts to the same real address or forging addresses, potentially flagging their accounts for suspicious behavior.
Address validation software contributes to Trust & Safety
Using additional trust and safety measures, like ID verification, is a compelling reason to choose one marketplace over another. These checks make users feel safer and more confident when making a transaction or sharing personal details. When faced with a choice between one P2P marketplace that makes an effort to verify user identity and another that doesn’t, the winner is clear.
People rely on their intuition in person to determine whether a business transaction is legitimate. Online, however, the red flags that would be obvious in person are hidden behind screens. Using address validation software is just one measure that platforms can adopt to help restore that sense of trust, reduce scams and ultimately deliver a much better customer experience.