The iGaming industry is regulated by various governmental and regulatory bodies around the world. The regulatory framework for iGaming varies from country to country, and in some cases, even from state to state within a country. However, there are some common regulatory elements that are typically present across most iGaming jurisdictions.
-
Licensing: iGaming operators must obtain a license from the appropriate regulatory body before they can offer their services to players. The licensing process typically involves background checks, financial audits, and other due diligence procedures to ensure that the operator is reputable and financially stable.
-
Game Certification: iGaming operators must have their games certified by independent testing laboratories to ensure that they are fair and random.
-
Responsible iGaming: Regulatory bodies often require iGaming operators to implement responsible iGaming policies and procedures to protect players from gambling-related harm.
-
Anti-Money Laundering (AML): iGaming operators are required to implement robust AML policies and procedures to prevent money laundering and terrorist financing.
-
Data Protection: iGaming operators must comply with data protection regulations and ensure that they protect players' personal and financial information.
-
Advertising Standards: iGaming operators must comply with advertising standards and regulations to ensure that their marketing materials are truthful, accurate, and not misleading.
-
Taxation: iGaming operators are typically subject to taxation in the jurisdictions where they operate.
Who is responsible for regulating the iGaming industry?
The regulation of the iGaming industry can vary depending on the country or region. In the United States, for example, the regulation of the iGaming industry is primarily the responsibility of individual states. Each state has its own regulatory body or commission that oversees iGaming activities and ensures compliance with state laws and regulations.
In other countries, the regulation of the iGaming industry may be the responsibility of a federal government agency or a specialized regulatory body. For example, in the United Kingdom, the Gambling Commission is the regulatory body responsible for overseeing all forms of gambling, including online iGaming and sports betting. In Australia, the Australian Communications and Media Authority (ACMA) is responsible for regulating online iGaming and enforcing the Interactive Gambling Act.
In some countries, the regulation of the iGaming industry may also involve collaboration between multiple government agencies, such as tax authorities, law enforcement agencies, and iGaming commissions. Overall, the regulatory landscape for the iGaming industry can be complex and multifaceted, and the responsible regulatory bodies may vary depending on the location and type of iGaming activity.
What is a player location check? Why is it required?
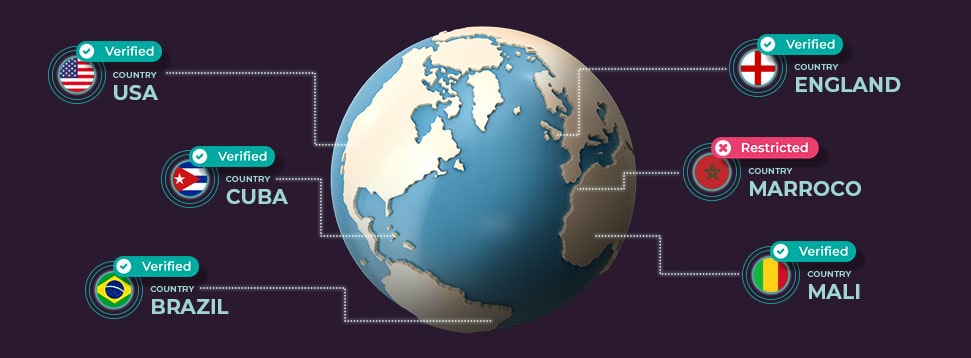
A player location check is a process used by iGaming operators to verify the physical location of a player at the time of gameplay. This is typically done using location data from the player's device, such as GPS, Wi-Fi triangulation, or IP geolocation. The purpose of a player location check is to ensure that the player is located in a jurisdiction where online iGaming is legal and authorized. This is required by law in many jurisdictions, as iGaming operators are required to comply with local regulations and prevent players from accessing their services from restricted areas. By verifying a player's location, operators can also prevent fraudulent activity, such as players using virtual private networks (VPNs) to circumvent geographic restrictions or engage in illegal activity. Overall, player location checks are a critical part of regulatory compliance for iGaming operators, and help ensure the integrity and fairness of their platforms.
How do iGaming regulators enforce player location checks?
iGaming regulators typically enforce player location checks through a combination of regulatory requirements, licensing agreements, and compliance monitoring. iGaming operators are required to comply with local laws and regulations, which often include requirements for verifying the physical location of players. Regulators may also require iGaming operators to obtain licenses or permits, which may include specific requirements for player location checks and compliance monitoring.
To enforce these requirements, iGaming regulators may conduct regular audits of iGaming operators to ensure compliance with local laws and regulations, and verify that player location checks are being performed correctly. They may also require operators to submit regular reports or data on player location checks and compliance efforts.
In addition, iGaming regulators may work with law enforcement agencies to investigate and prosecute cases of illegal online iGaming, including cases where players are located in restricted jurisdictions or using fraudulent means to access iGaming platforms. Regulators may also impose fines or other penalties on iGaming operators who fail to comply with player location check requirements or other regulatory requirements.
What actions can iGaming regulators take if an operator fails to comply with regulations?
When iGaming operators fail to comply with regulations, iGaming regulators can take a range of actions to ensure adherence and enforce penalties. The specific measures taken depend on the nature and severity of the violation, as well as the regulatory framework in place.
One potential consequence for non-compliance is the imposition of fines and penalties. iGaming regulators can levy significant fines on operators who do not adhere to regulations, with the amount potentially increasing for repeated violations.
In more severe cases, iGaming regulators might suspend or revoke an iGaming operator's license. This action not only prevents the operator from offering iGaming services but can also have substantial financial and reputational repercussions.
To ensure ongoing compliance, iGaming regulators may require operators to undergo regular compliance monitoring. This process can involve audits, inspections, and reporting requirements that help maintain adherence to regulations.
In instances of serious or persistent violations, iGaming regulators may choose to pursue legal action against the iGaming operator. Depending on the nature of the violation, this could entail civil or criminal charges, further emphasizing the importance of compliance in the iGaming industry.